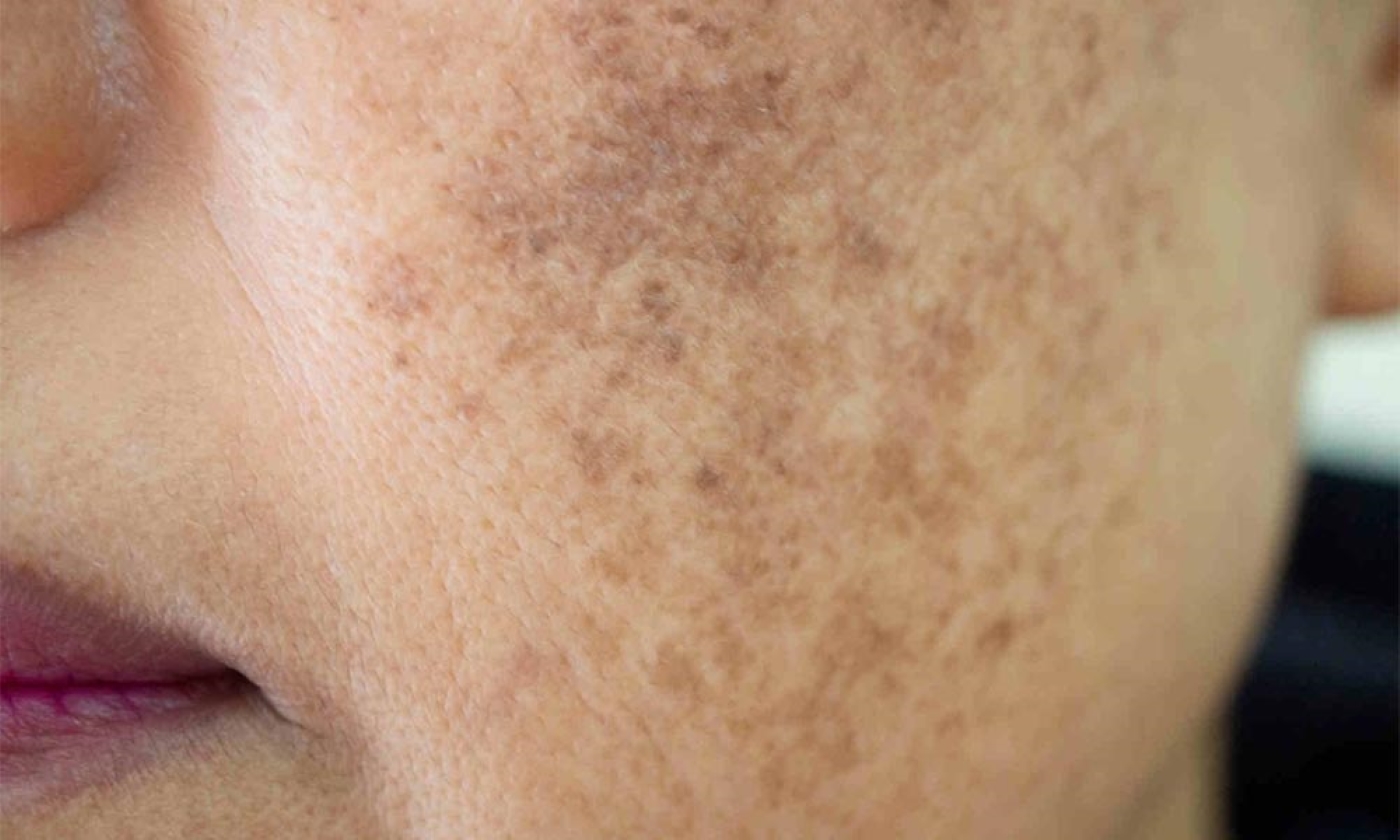
Pigmentation
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, hair, and eyes caused by melanin, a natural pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. There are different types of pigmentation, and its levels vary from person to person. Common pigmentation disorders include:
Hyperpigmentation:
This condition occurs when an excess of melanin is produced, leading to darker patches of skin. It can be caused by sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin injuries. Common types of hyperpigmentation include melasma, age spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Hypopigmentation:
This condition results in patches of skin that are lighter than the surrounding areas due to reduced melanin production. Conditions like vitiligo and albinism are examples of hypopigmentation disorders.
Melasma:
A form of hyperpigmentation often triggered by hormonal changes, pregnancy, or birth control pills. It appears as brown or gray patches, commonly on the face.
Pigmentation treatments include topical creams, laser therapy, chemical peels, and microdermabrasion. Preventative measures, like using sunscreen and avoiding excessive sun exposure, are essential in managing pigmentation concerns.
