Fungal Infections
Fungal infections occur when fungi invade a part of the body and overwhelm the immune system. Fungi are organisms that can thrive in different environments, and some can live naturally on the skin. However, when they multiply uncontrollably or penetrate deeper tissues, they cause infections.
Causes of Fungal Infections
Warm, moist environments: Fungi thrive in damp areas, such as sweaty skin folds.
Weakened immune system: People with compromised immune systems (e.g., those with HIV, cancer, diabetes, or taking immunosuppressive drugs) are more susceptible.
Poor hygiene: Not washing skin properly or wearing unclean clothing can promote fungal growth.
Common Types of Fungal Infections
1. Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis):
Cause: Caused by dermatophyte fungi, athlete’s foot affects the skin of the feet, particularly between the toes.
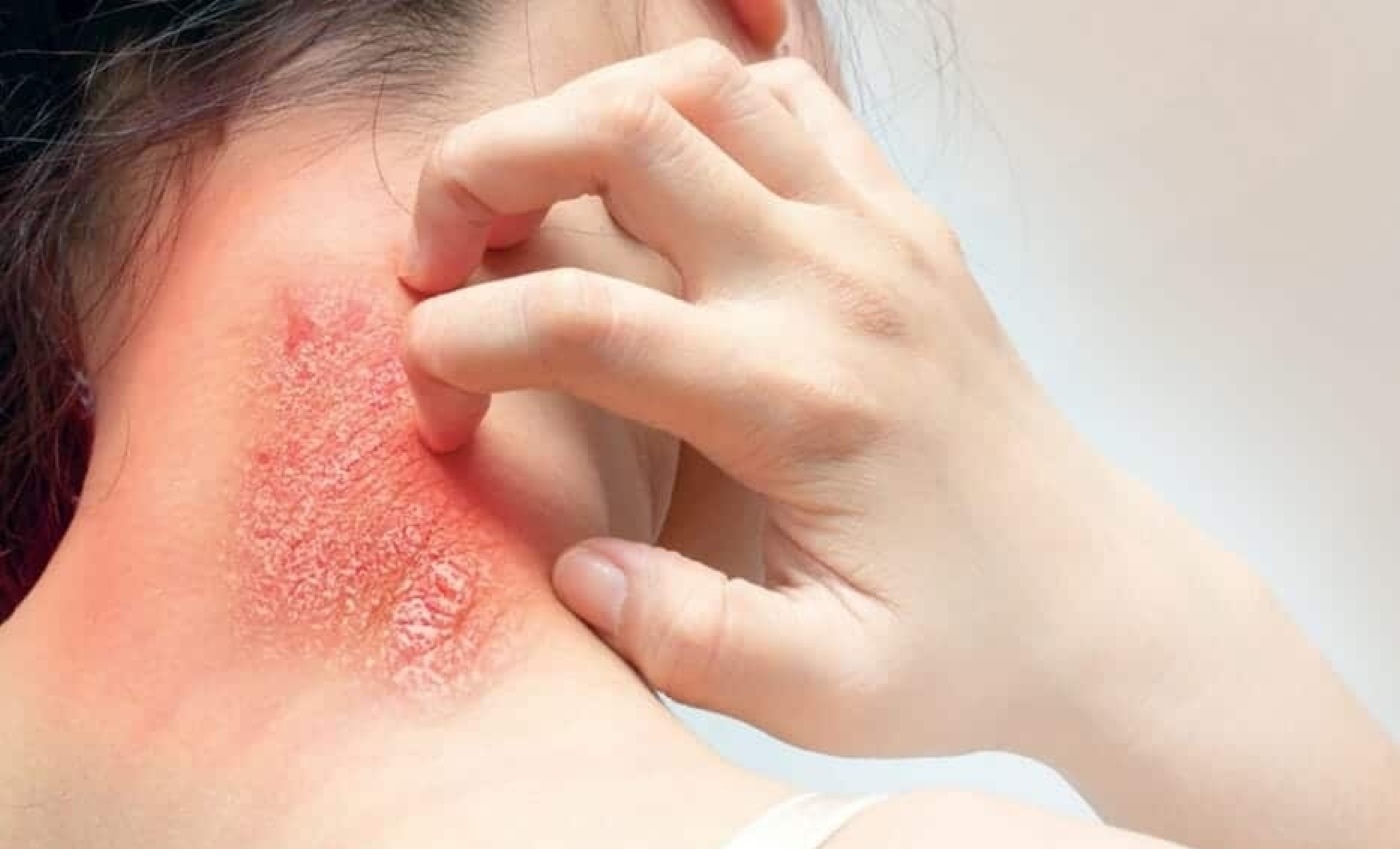
Symptoms: Redness, itching, peeling skin, cracking, and sometimes blisters.
Transmission: Common in shared spaces like locker rooms or swimming pools.
Treatment: Topical antifungal creams or powders, and keeping feet dry and clean.
2. Ringworm (Tinea Corporis):
Cause: Also caused by dermatophytes, ringworm can occur on any part of the body and is not caused by worms, despite the name.
Symptoms: Ring-shaped, red, scaly patches with a clear center. Itching and inflammation are common.
Transmission: Spread through direct skin contact or sharing contaminated items like towels and clothing.
Treatment: Antifungal creams or oral medications.
