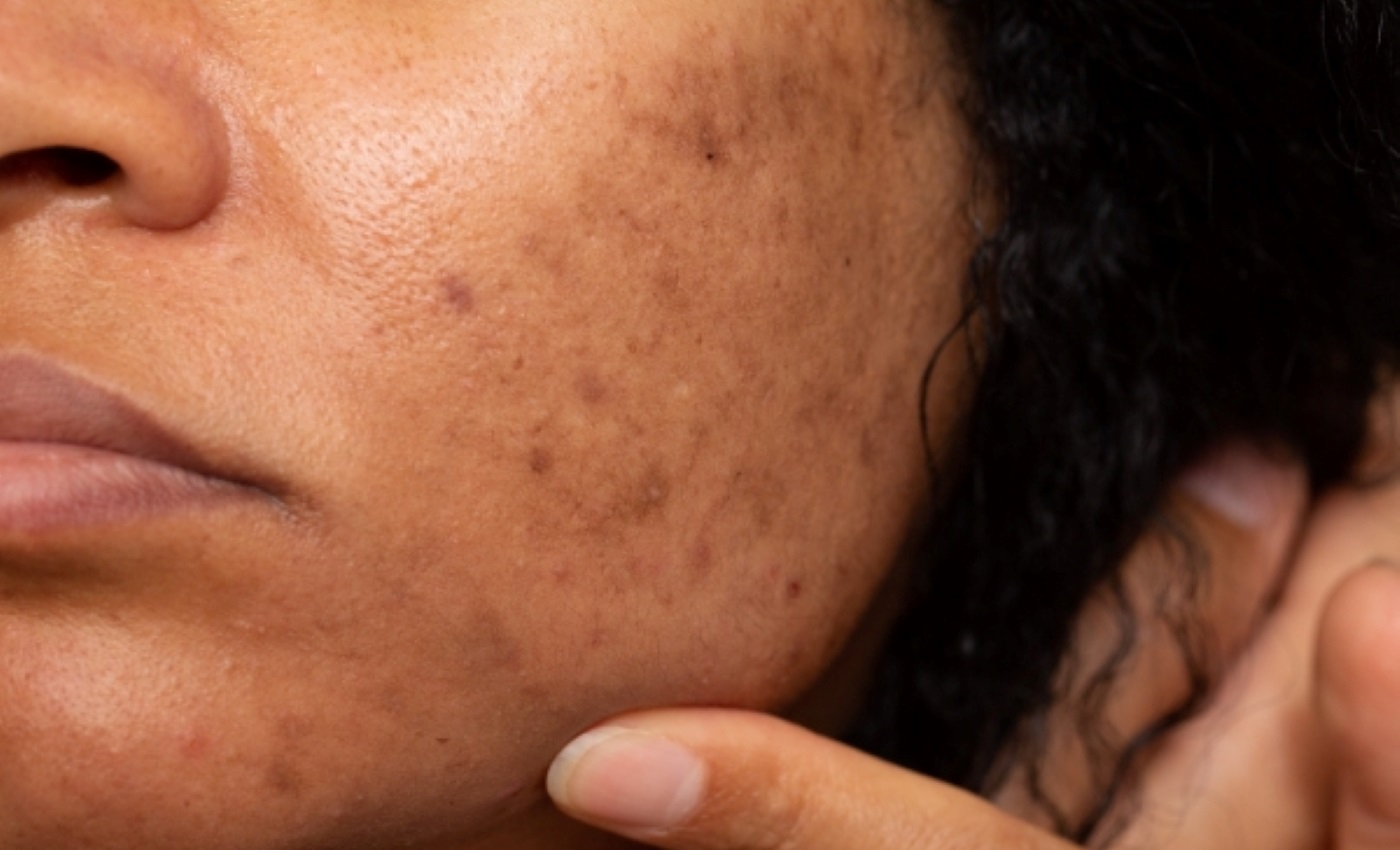
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation refers to darkening of the skin caused by an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. It can appear in small patches, cover large areas, or affect the entire body. Although generally harmless, hyperpigmentation can cause emotional distress and cosmetic concerns, leading many to seek treatment to reduce or eliminate it.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation can be triggered by various internal and external factors, including:
1. Sun Exposure:
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun stimulates the production of melanin as the skin’s natural defense mechanism. Over time, repeated sun exposure can lead to sunspots or age spots, which are a form of hyperpigmentation.
2. Inflammation and Skin Injury:
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) occurs after an injury or inflammation to the skin, such as acne, eczema, or cuts. The skin responds by producing excess melanin in the affected area.
3. Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can lead to a type of hyperpigmentation called melasma. This often occurs during pregnancy (commonly referred to as the "mask of pregnancy"), with the use of birth control pills, or due to hormone replacement therapy.
4. Medications:
Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, antimalarials, and some antibiotics, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
